Is HostGator storing my password in plaintext? The Next CEO of Stack OverflowHow up-to-date is the plaintextoffenders list?Is it better to hash n*x times in sha1 or n times in sha512 on the client side?Definitely safest password storage scheme?Forgot Password? - sends email with plaintext passwordIs it ok for software to store passwords locally in plain-text?Finding Plaintext Password RepositoriesHow to avoid storing plaintext during CHAP authenticationReceived an email about an “Etsy” Password Reset due to the “Linkedin Breach…” is this a phishing attempt?Storing Password Hash plaintextThird party program is storing a password in a DSN. Is it a security threat?Methods for storing plaintext passwords on a client
Why do remote companies require working in the US?
What does this shorthand mean?
Term for the "extreme-extension" version of a straw man fallacy?
Can the Reverse Gravity spell affect the Meteor Swarm spell?
How can I open an app using Terminal?
Why is there a PLL in CPU?
Why does GHC infer a monomorphic type here, even with MonomorphismRestriction disabled?
Was a professor correct to chastise me for writing "Prof. X" rather than "Professor X"?
Why Were Madagascar and New Zealand Discovered So Late?
What makes a siege story/plot interesting?
I believe this to be a fraud - hired, then asked to cash check and send cash as Bitcoin
WOW air has ceased operation, can I get my tickets refunded?
How easy is it to start Magic from scratch?
When airplanes disconnect from a tanker during air to air refueling, why do they bank so sharply to the right?
Grabbing quick drinks
How to be diplomatic in refusing to write code that breaches the privacy of our users
Can a caster that cast Polymorph on themselves stop concentrating at any point even if their Int is low?
Why is Miller's case titled R (Miller)?
Science fiction novels about a solar system spanning civilisation where people change their bodies at will
% symbol leads to superlong (forever?) compilations
Why didn't Theresa May consult with Parliament before negotiating a deal with the EU?
Would this house-rule that treats advantage as a +1 to the roll instead (and disadvantage as -1) and allows them to stack be balanced?
Rotate a column
Solution of this Diophantine Equation
Is HostGator storing my password in plaintext?
The Next CEO of Stack OverflowHow up-to-date is the plaintextoffenders list?Is it better to hash n*x times in sha1 or n times in sha512 on the client side?Definitely safest password storage scheme?Forgot Password? - sends email with plaintext passwordIs it ok for software to store passwords locally in plain-text?Finding Plaintext Password RepositoriesHow to avoid storing plaintext during CHAP authenticationReceived an email about an “Etsy” Password Reset due to the “Linkedin Breach…” is this a phishing attempt?Storing Password Hash plaintextThird party program is storing a password in a DSN. Is it a security threat?Methods for storing plaintext passwords on a client
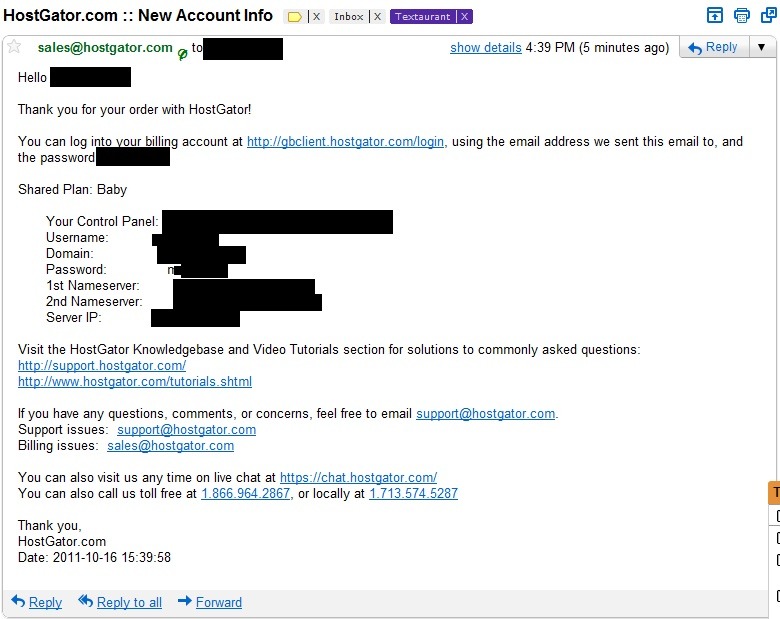
I want to bring this up to HostGator, but want to verify my suspicions before making a big fuss.
I asked a customer care representative to help me add an SSL certificate to a site I host with them. When he was done, I received this e-mail with all my login information, and my entire password in plain text (I left the first letter visible as evidence). I set up this password over a year ago, and it was a big surprise to find out they sent it back to me, unprompted, in plaintext:

I immediately brought this up to the representative, who repeatedly tried to convince me that it was OK. I decided to drop it after a few minutes, because I think I should bring it up to someone higher up. Before I do so, is it safe to assume that my password is stored in their database as plain text? If so, do you have any suggestions on how to address this issue with the provider?

passwords databases web-hosting
New contributor
Marquizzo is a new contributor to this site. Take care in asking for clarification, commenting, and answering.
Check out our Code of Conduct.
add a comment |
I want to bring this up to HostGator, but want to verify my suspicions before making a big fuss.
I asked a customer care representative to help me add an SSL certificate to a site I host with them. When he was done, I received this e-mail with all my login information, and my entire password in plain text (I left the first letter visible as evidence). I set up this password over a year ago, and it was a big surprise to find out they sent it back to me, unprompted, in plaintext:

I immediately brought this up to the representative, who repeatedly tried to convince me that it was OK. I decided to drop it after a few minutes, because I think I should bring it up to someone higher up. Before I do so, is it safe to assume that my password is stored in their database as plain text? If so, do you have any suggestions on how to address this issue with the provider?

passwords databases web-hosting
New contributor
Marquizzo is a new contributor to this site. Take care in asking for clarification, commenting, and answering.
Check out our Code of Conduct.
Comments are not for extended discussion; this conversation has been moved to chat.
– Rory Alsop♦
9 hours ago
add a comment |
I want to bring this up to HostGator, but want to verify my suspicions before making a big fuss.
I asked a customer care representative to help me add an SSL certificate to a site I host with them. When he was done, I received this e-mail with all my login information, and my entire password in plain text (I left the first letter visible as evidence). I set up this password over a year ago, and it was a big surprise to find out they sent it back to me, unprompted, in plaintext:

I immediately brought this up to the representative, who repeatedly tried to convince me that it was OK. I decided to drop it after a few minutes, because I think I should bring it up to someone higher up. Before I do so, is it safe to assume that my password is stored in their database as plain text? If so, do you have any suggestions on how to address this issue with the provider?

passwords databases web-hosting
New contributor
Marquizzo is a new contributor to this site. Take care in asking for clarification, commenting, and answering.
Check out our Code of Conduct.
I want to bring this up to HostGator, but want to verify my suspicions before making a big fuss.
I asked a customer care representative to help me add an SSL certificate to a site I host with them. When he was done, I received this e-mail with all my login information, and my entire password in plain text (I left the first letter visible as evidence). I set up this password over a year ago, and it was a big surprise to find out they sent it back to me, unprompted, in plaintext:

I immediately brought this up to the representative, who repeatedly tried to convince me that it was OK. I decided to drop it after a few minutes, because I think I should bring it up to someone higher up. Before I do so, is it safe to assume that my password is stored in their database as plain text? If so, do you have any suggestions on how to address this issue with the provider?

passwords databases web-hosting
passwords databases web-hosting
New contributor
Marquizzo is a new contributor to this site. Take care in asking for clarification, commenting, and answering.
Check out our Code of Conduct.
New contributor
Marquizzo is a new contributor to this site. Take care in asking for clarification, commenting, and answering.
Check out our Code of Conduct.
edited 2 days ago
Marquizzo
New contributor
Marquizzo is a new contributor to this site. Take care in asking for clarification, commenting, and answering.
Check out our Code of Conduct.
asked 2 days ago
MarquizzoMarquizzo
474129
474129
New contributor
Marquizzo is a new contributor to this site. Take care in asking for clarification, commenting, and answering.
Check out our Code of Conduct.
New contributor
Marquizzo is a new contributor to this site. Take care in asking for clarification, commenting, and answering.
Check out our Code of Conduct.
Marquizzo is a new contributor to this site. Take care in asking for clarification, commenting, and answering.
Check out our Code of Conduct.
Comments are not for extended discussion; this conversation has been moved to chat.
– Rory Alsop♦
9 hours ago
add a comment |
Comments are not for extended discussion; this conversation has been moved to chat.
– Rory Alsop♦
9 hours ago
Comments are not for extended discussion; this conversation has been moved to chat.
– Rory Alsop♦
9 hours ago
Comments are not for extended discussion; this conversation has been moved to chat.
– Rory Alsop♦
9 hours ago
add a comment |
3 Answers
3
active
oldest
votes
Yep, that's a big problem, especially if that was your old password (i.e. not a newly assigned one).
Technically, the password might be stored under reversible encryption rather than plain text, but that's nearly as bad. The absolute minimum standard should be a salted hash - anything less and anybody with access to the auth database who wants to can use an online rainbow table to get back the plaintext passwords in moments - but single-iteration secure hash algorithm (SHA) functions are still easy to brute force with a GPU (they're designed to be fast; a high-end GPU can compute billions per second) so they really ought to be using a proper password hashing function such as scrypt or argon2, or in a pinch bcrypt or PBKDF2.
Also, there is absolutely no way to guarantee that the email was encrypted along the entire path between their mail server and your email client. Email was designed in a day when people didn't really consider such things to be critical, and short of an end-to-end encryption scheme like OpenPGP or S/MIME, email is at best encrypted opportunistically, and may be passed through an unencrypted relay.
25
That's a very good point. Not only are they storing their passwords in a potentially insecure manner, they are also unnecessarily transmitting them to their users through an insecure protocol.
– Marquizzo
2 days ago
32
You should absolutely bring this up. No decent current security system should be able to provide current credentials. Admins should have knowledge on how to reset to a default as necessary or provide reset instructions, but not retrieve and provide you with the private credentials that you, the user, created, and should only be known by you. You can bring this up as an exposure to a malicious insider or MITM.
– psosuna
yesterday
7
I'd change the first sentence to "... if that was any user-provided password" to catch the broadest sense. Only autogenerated passwords that must be changed at next login are okay(ish) to transmit this way.
– orithena
yesterday
9
This answer could be stronger. The rep was completely wrong. Even if they are using reversible encryption so they can extract the original plaintext, that's about as good as not encrypting at all and he claims that email is secure which is total nonsense. This needs to be escalated with HostGator for the benefit of everybody.
– Lightness Races in Orbit
yesterday
3
Why do you say "in a pinch, bcrypt" - is it not just as secure as scrypt or argon2? It certainly has years of field testing.
– corsiKa
yesterday
|
show 6 more comments
Yes, they store passwords in plaintext. This was discovered in 2011.
This is confirmed HostGator being listed on Plaintext Offenders, as well as by its entry in the CVS file containing a list of offenders. This is not new and has been known since at least 2011. HostGator has not reformed since. The Plaintext Offenders website shows a screenshot similar to yours as evidence:
1
I realize that this is a semantic point, but I don't see how this proves that they store passwords in plaintext. They could have them encrypted and are decrypting them when they send them to you. Of course this is bad practice.
– Greg Schmit
6 hours ago
1
And they claim, at least, that they don't store passwords in plaintext: i.imgur.com/9qrVPrm.png (again, not disputing that this is bad practice).
– Greg Schmit
6 hours ago
@GregSchmit: Regardless of whether the password is stored plaintext in the auth database, it is stored plaintext in HostGator's e-mail server, potentially transmitted in plaintext across the Internet, and potentially stored plaintext at the recipient e-mail server. I say potentially because it largely depends on the domain where you receive your HostGator e-mail and how the server handling that domain is configured.
– Ben Voigt
3 hours ago
1
@BenVoigt We already know for a fact that the plaintext password was emailed, so that's irrelevant. The question is whether they are storing that in plaintext in their database. The OP wouldn't have asked "is this password stored in plaintext on an email server somewhere", because that would be a stupid question to ask given that the password was emailed.
– Greg Schmit
3 hours ago
@GregSchmit: Why can't OP ask a question he already knows the answer to? That's Socratic method. The goal is not to learn the answer, it's to make the other person aware of the problem.
– Ben Voigt
3 hours ago
|
show 1 more comment
If the company rep's response is true, the Password is stored as an encrypted text. This makes the plain text password in unprompted email a bigger concern.
is it safe to assume that my password is stored in their database as plain text?
The company representative explicitly told that they are not storing the password in plain text. Assuming that he is telling the truth, my conclusion is that they are storing the password in encrypted text. They are better than plain text passwords but they are still insecure. Hashing and salting is the best way to store passwords.
If the stored password is encrypted, the biggest concern here is not the way it is stored but the way it is transmitted, in plain text on an email when the user did not request any.
do you have any suggestions on how to address this issue with the
provider?
You can ask the company to change the following (in the order of priority)
- Stop sending passwords over email.
- Provide Reset password option instead of recovering it.
- Replace encrypting passwords with Hashing and Salting.
In response to comments,
- Yes, there is high chance that the rep is lying or didn't know what he is talking about. But there is also a possibility that he was telling the truth. This answer deals with that scenario.
- I consider transmission of passwords as a bigger problem to storage because the OP was sent the password in an email when he did not ask for any.
- I have seen systems that store passwords in an encrypted text and send them to users upon request. They are not secure, but they do exist. Just because you received your info in plain text does not guarantee it is stored that way too.
40
"No, the company representative explicitly told that they are not storing the password in plain text" since when can you blindly trust what a low level rep says about a large company?
– MindSwipe
yesterday
36
@KolappanNathan Given that that same employee considers sending passwords via email to be a safe practice, there's very little reason to assume that rep is a trustworthy source of information.
– Beofett
yesterday
17
"Assuming he is telling the truth" implies he is either truthful and correct or lying. The reality is likely a third option: he doesn't actually know the answer and, like many reps, is simply trying to make the person on the other end happy. Never attribute to malice what can easily be explained by ignorance. The fact that the rep doesn't even know how to spell encryption (the way they spelled it clearly wasn't the result of a simply typo) is a strong indication that they are simply ignorant of this topic and don't know anything about it.
– Conor Mancone
yesterday
2
@ConorMancone That is possible and an answer already exists for such a possibility. My answer deals with an another possible scenario that the password is encrypted. It is a possible scenario. No one can tell for 100% percent that the password is in plain text. What is wrong about writing answers for an another possible scenario? The typo does not indicate anything. He misspelled a single letter!!!
– Kolappan Nathan
yesterday
2
@ConorMancone The OP said that he received the password in email when he did not ask for any. He could have abandoned his email. I consider transmission to be biggest issue. I agree with the fact that encrypting passwords is insecure too. No disagreements there.
– Kolappan Nathan
yesterday
|
show 7 more comments
Your Answer
StackExchange.ready(function()
var channelOptions =
tags: "".split(" "),
id: "162"
;
initTagRenderer("".split(" "), "".split(" "), channelOptions);
StackExchange.using("externalEditor", function()
// Have to fire editor after snippets, if snippets enabled
if (StackExchange.settings.snippets.snippetsEnabled)
StackExchange.using("snippets", function()
createEditor();
);
else
createEditor();
);
function createEditor()
StackExchange.prepareEditor(
heartbeatType: 'answer',
autoActivateHeartbeat: false,
convertImagesToLinks: false,
noModals: true,
showLowRepImageUploadWarning: true,
reputationToPostImages: null,
bindNavPrevention: true,
postfix: "",
imageUploader:
brandingHtml: "Powered by u003ca class="icon-imgur-white" href="https://imgur.com/"u003eu003c/au003e",
contentPolicyHtml: "User contributions licensed under u003ca href="https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/3.0/"u003ecc by-sa 3.0 with attribution requiredu003c/au003e u003ca href="https://stackoverflow.com/legal/content-policy"u003e(content policy)u003c/au003e",
allowUrls: true
,
noCode: true, onDemand: true,
discardSelector: ".discard-answer"
,immediatelyShowMarkdownHelp:true
);
);
Marquizzo is a new contributor. Be nice, and check out our Code of Conduct.
Sign up or log in
StackExchange.ready(function ()
StackExchange.helpers.onClickDraftSave('#login-link');
);
Sign up using Google
Sign up using Facebook
Sign up using Email and Password
Post as a guest
Required, but never shown
StackExchange.ready(
function ()
StackExchange.openid.initPostLogin('.new-post-login', 'https%3a%2f%2fsecurity.stackexchange.com%2fquestions%2f206186%2fis-hostgator-storing-my-password-in-plaintext%23new-answer', 'question_page');
);
Post as a guest
Required, but never shown
3 Answers
3
active
oldest
votes
3 Answers
3
active
oldest
votes
active
oldest
votes
active
oldest
votes
Yep, that's a big problem, especially if that was your old password (i.e. not a newly assigned one).
Technically, the password might be stored under reversible encryption rather than plain text, but that's nearly as bad. The absolute minimum standard should be a salted hash - anything less and anybody with access to the auth database who wants to can use an online rainbow table to get back the plaintext passwords in moments - but single-iteration secure hash algorithm (SHA) functions are still easy to brute force with a GPU (they're designed to be fast; a high-end GPU can compute billions per second) so they really ought to be using a proper password hashing function such as scrypt or argon2, or in a pinch bcrypt or PBKDF2.
Also, there is absolutely no way to guarantee that the email was encrypted along the entire path between their mail server and your email client. Email was designed in a day when people didn't really consider such things to be critical, and short of an end-to-end encryption scheme like OpenPGP or S/MIME, email is at best encrypted opportunistically, and may be passed through an unencrypted relay.
25
That's a very good point. Not only are they storing their passwords in a potentially insecure manner, they are also unnecessarily transmitting them to their users through an insecure protocol.
– Marquizzo
2 days ago
32
You should absolutely bring this up. No decent current security system should be able to provide current credentials. Admins should have knowledge on how to reset to a default as necessary or provide reset instructions, but not retrieve and provide you with the private credentials that you, the user, created, and should only be known by you. You can bring this up as an exposure to a malicious insider or MITM.
– psosuna
yesterday
7
I'd change the first sentence to "... if that was any user-provided password" to catch the broadest sense. Only autogenerated passwords that must be changed at next login are okay(ish) to transmit this way.
– orithena
yesterday
9
This answer could be stronger. The rep was completely wrong. Even if they are using reversible encryption so they can extract the original plaintext, that's about as good as not encrypting at all and he claims that email is secure which is total nonsense. This needs to be escalated with HostGator for the benefit of everybody.
– Lightness Races in Orbit
yesterday
3
Why do you say "in a pinch, bcrypt" - is it not just as secure as scrypt or argon2? It certainly has years of field testing.
– corsiKa
yesterday
|
show 6 more comments
Yep, that's a big problem, especially if that was your old password (i.e. not a newly assigned one).
Technically, the password might be stored under reversible encryption rather than plain text, but that's nearly as bad. The absolute minimum standard should be a salted hash - anything less and anybody with access to the auth database who wants to can use an online rainbow table to get back the plaintext passwords in moments - but single-iteration secure hash algorithm (SHA) functions are still easy to brute force with a GPU (they're designed to be fast; a high-end GPU can compute billions per second) so they really ought to be using a proper password hashing function such as scrypt or argon2, or in a pinch bcrypt or PBKDF2.
Also, there is absolutely no way to guarantee that the email was encrypted along the entire path between their mail server and your email client. Email was designed in a day when people didn't really consider such things to be critical, and short of an end-to-end encryption scheme like OpenPGP or S/MIME, email is at best encrypted opportunistically, and may be passed through an unencrypted relay.
25
That's a very good point. Not only are they storing their passwords in a potentially insecure manner, they are also unnecessarily transmitting them to their users through an insecure protocol.
– Marquizzo
2 days ago
32
You should absolutely bring this up. No decent current security system should be able to provide current credentials. Admins should have knowledge on how to reset to a default as necessary or provide reset instructions, but not retrieve and provide you with the private credentials that you, the user, created, and should only be known by you. You can bring this up as an exposure to a malicious insider or MITM.
– psosuna
yesterday
7
I'd change the first sentence to "... if that was any user-provided password" to catch the broadest sense. Only autogenerated passwords that must be changed at next login are okay(ish) to transmit this way.
– orithena
yesterday
9
This answer could be stronger. The rep was completely wrong. Even if they are using reversible encryption so they can extract the original plaintext, that's about as good as not encrypting at all and he claims that email is secure which is total nonsense. This needs to be escalated with HostGator for the benefit of everybody.
– Lightness Races in Orbit
yesterday
3
Why do you say "in a pinch, bcrypt" - is it not just as secure as scrypt or argon2? It certainly has years of field testing.
– corsiKa
yesterday
|
show 6 more comments
Yep, that's a big problem, especially if that was your old password (i.e. not a newly assigned one).
Technically, the password might be stored under reversible encryption rather than plain text, but that's nearly as bad. The absolute minimum standard should be a salted hash - anything less and anybody with access to the auth database who wants to can use an online rainbow table to get back the plaintext passwords in moments - but single-iteration secure hash algorithm (SHA) functions are still easy to brute force with a GPU (they're designed to be fast; a high-end GPU can compute billions per second) so they really ought to be using a proper password hashing function such as scrypt or argon2, or in a pinch bcrypt or PBKDF2.
Also, there is absolutely no way to guarantee that the email was encrypted along the entire path between their mail server and your email client. Email was designed in a day when people didn't really consider such things to be critical, and short of an end-to-end encryption scheme like OpenPGP or S/MIME, email is at best encrypted opportunistically, and may be passed through an unencrypted relay.
Yep, that's a big problem, especially if that was your old password (i.e. not a newly assigned one).
Technically, the password might be stored under reversible encryption rather than plain text, but that's nearly as bad. The absolute minimum standard should be a salted hash - anything less and anybody with access to the auth database who wants to can use an online rainbow table to get back the plaintext passwords in moments - but single-iteration secure hash algorithm (SHA) functions are still easy to brute force with a GPU (they're designed to be fast; a high-end GPU can compute billions per second) so they really ought to be using a proper password hashing function such as scrypt or argon2, or in a pinch bcrypt or PBKDF2.
Also, there is absolutely no way to guarantee that the email was encrypted along the entire path between their mail server and your email client. Email was designed in a day when people didn't really consider such things to be critical, and short of an end-to-end encryption scheme like OpenPGP or S/MIME, email is at best encrypted opportunistically, and may be passed through an unencrypted relay.
answered 2 days ago
CBHackingCBHacking
11.2k21929
11.2k21929
25
That's a very good point. Not only are they storing their passwords in a potentially insecure manner, they are also unnecessarily transmitting them to their users through an insecure protocol.
– Marquizzo
2 days ago
32
You should absolutely bring this up. No decent current security system should be able to provide current credentials. Admins should have knowledge on how to reset to a default as necessary or provide reset instructions, but not retrieve and provide you with the private credentials that you, the user, created, and should only be known by you. You can bring this up as an exposure to a malicious insider or MITM.
– psosuna
yesterday
7
I'd change the first sentence to "... if that was any user-provided password" to catch the broadest sense. Only autogenerated passwords that must be changed at next login are okay(ish) to transmit this way.
– orithena
yesterday
9
This answer could be stronger. The rep was completely wrong. Even if they are using reversible encryption so they can extract the original plaintext, that's about as good as not encrypting at all and he claims that email is secure which is total nonsense. This needs to be escalated with HostGator for the benefit of everybody.
– Lightness Races in Orbit
yesterday
3
Why do you say "in a pinch, bcrypt" - is it not just as secure as scrypt or argon2? It certainly has years of field testing.
– corsiKa
yesterday
|
show 6 more comments
25
That's a very good point. Not only are they storing their passwords in a potentially insecure manner, they are also unnecessarily transmitting them to their users through an insecure protocol.
– Marquizzo
2 days ago
32
You should absolutely bring this up. No decent current security system should be able to provide current credentials. Admins should have knowledge on how to reset to a default as necessary or provide reset instructions, but not retrieve and provide you with the private credentials that you, the user, created, and should only be known by you. You can bring this up as an exposure to a malicious insider or MITM.
– psosuna
yesterday
7
I'd change the first sentence to "... if that was any user-provided password" to catch the broadest sense. Only autogenerated passwords that must be changed at next login are okay(ish) to transmit this way.
– orithena
yesterday
9
This answer could be stronger. The rep was completely wrong. Even if they are using reversible encryption so they can extract the original plaintext, that's about as good as not encrypting at all and he claims that email is secure which is total nonsense. This needs to be escalated with HostGator for the benefit of everybody.
– Lightness Races in Orbit
yesterday
3
Why do you say "in a pinch, bcrypt" - is it not just as secure as scrypt or argon2? It certainly has years of field testing.
– corsiKa
yesterday
25
25
That's a very good point. Not only are they storing their passwords in a potentially insecure manner, they are also unnecessarily transmitting them to their users through an insecure protocol.
– Marquizzo
2 days ago
That's a very good point. Not only are they storing their passwords in a potentially insecure manner, they are also unnecessarily transmitting them to their users through an insecure protocol.
– Marquizzo
2 days ago
32
32
You should absolutely bring this up. No decent current security system should be able to provide current credentials. Admins should have knowledge on how to reset to a default as necessary or provide reset instructions, but not retrieve and provide you with the private credentials that you, the user, created, and should only be known by you. You can bring this up as an exposure to a malicious insider or MITM.
– psosuna
yesterday
You should absolutely bring this up. No decent current security system should be able to provide current credentials. Admins should have knowledge on how to reset to a default as necessary or provide reset instructions, but not retrieve and provide you with the private credentials that you, the user, created, and should only be known by you. You can bring this up as an exposure to a malicious insider or MITM.
– psosuna
yesterday
7
7
I'd change the first sentence to "... if that was any user-provided password" to catch the broadest sense. Only autogenerated passwords that must be changed at next login are okay(ish) to transmit this way.
– orithena
yesterday
I'd change the first sentence to "... if that was any user-provided password" to catch the broadest sense. Only autogenerated passwords that must be changed at next login are okay(ish) to transmit this way.
– orithena
yesterday
9
9
This answer could be stronger. The rep was completely wrong. Even if they are using reversible encryption so they can extract the original plaintext, that's about as good as not encrypting at all and he claims that email is secure which is total nonsense. This needs to be escalated with HostGator for the benefit of everybody.
– Lightness Races in Orbit
yesterday
This answer could be stronger. The rep was completely wrong. Even if they are using reversible encryption so they can extract the original plaintext, that's about as good as not encrypting at all and he claims that email is secure which is total nonsense. This needs to be escalated with HostGator for the benefit of everybody.
– Lightness Races in Orbit
yesterday
3
3
Why do you say "in a pinch, bcrypt" - is it not just as secure as scrypt or argon2? It certainly has years of field testing.
– corsiKa
yesterday
Why do you say "in a pinch, bcrypt" - is it not just as secure as scrypt or argon2? It certainly has years of field testing.
– corsiKa
yesterday
|
show 6 more comments
Yes, they store passwords in plaintext. This was discovered in 2011.
This is confirmed HostGator being listed on Plaintext Offenders, as well as by its entry in the CVS file containing a list of offenders. This is not new and has been known since at least 2011. HostGator has not reformed since. The Plaintext Offenders website shows a screenshot similar to yours as evidence:

1
I realize that this is a semantic point, but I don't see how this proves that they store passwords in plaintext. They could have them encrypted and are decrypting them when they send them to you. Of course this is bad practice.
– Greg Schmit
6 hours ago
1
And they claim, at least, that they don't store passwords in plaintext: i.imgur.com/9qrVPrm.png (again, not disputing that this is bad practice).
– Greg Schmit
6 hours ago
@GregSchmit: Regardless of whether the password is stored plaintext in the auth database, it is stored plaintext in HostGator's e-mail server, potentially transmitted in plaintext across the Internet, and potentially stored plaintext at the recipient e-mail server. I say potentially because it largely depends on the domain where you receive your HostGator e-mail and how the server handling that domain is configured.
– Ben Voigt
3 hours ago
1
@BenVoigt We already know for a fact that the plaintext password was emailed, so that's irrelevant. The question is whether they are storing that in plaintext in their database. The OP wouldn't have asked "is this password stored in plaintext on an email server somewhere", because that would be a stupid question to ask given that the password was emailed.
– Greg Schmit
3 hours ago
@GregSchmit: Why can't OP ask a question he already knows the answer to? That's Socratic method. The goal is not to learn the answer, it's to make the other person aware of the problem.
– Ben Voigt
3 hours ago
|
show 1 more comment
Yes, they store passwords in plaintext. This was discovered in 2011.
This is confirmed HostGator being listed on Plaintext Offenders, as well as by its entry in the CVS file containing a list of offenders. This is not new and has been known since at least 2011. HostGator has not reformed since. The Plaintext Offenders website shows a screenshot similar to yours as evidence:

1
I realize that this is a semantic point, but I don't see how this proves that they store passwords in plaintext. They could have them encrypted and are decrypting them when they send them to you. Of course this is bad practice.
– Greg Schmit
6 hours ago
1
And they claim, at least, that they don't store passwords in plaintext: i.imgur.com/9qrVPrm.png (again, not disputing that this is bad practice).
– Greg Schmit
6 hours ago
@GregSchmit: Regardless of whether the password is stored plaintext in the auth database, it is stored plaintext in HostGator's e-mail server, potentially transmitted in plaintext across the Internet, and potentially stored plaintext at the recipient e-mail server. I say potentially because it largely depends on the domain where you receive your HostGator e-mail and how the server handling that domain is configured.
– Ben Voigt
3 hours ago
1
@BenVoigt We already know for a fact that the plaintext password was emailed, so that's irrelevant. The question is whether they are storing that in plaintext in their database. The OP wouldn't have asked "is this password stored in plaintext on an email server somewhere", because that would be a stupid question to ask given that the password was emailed.
– Greg Schmit
3 hours ago
@GregSchmit: Why can't OP ask a question he already knows the answer to? That's Socratic method. The goal is not to learn the answer, it's to make the other person aware of the problem.
– Ben Voigt
3 hours ago
|
show 1 more comment
Yes, they store passwords in plaintext. This was discovered in 2011.
This is confirmed HostGator being listed on Plaintext Offenders, as well as by its entry in the CVS file containing a list of offenders. This is not new and has been known since at least 2011. HostGator has not reformed since. The Plaintext Offenders website shows a screenshot similar to yours as evidence:

Yes, they store passwords in plaintext. This was discovered in 2011.
This is confirmed HostGator being listed on Plaintext Offenders, as well as by its entry in the CVS file containing a list of offenders. This is not new and has been known since at least 2011. HostGator has not reformed since. The Plaintext Offenders website shows a screenshot similar to yours as evidence:

answered 22 hours ago
forestforest
38.8k18127139
38.8k18127139
1
I realize that this is a semantic point, but I don't see how this proves that they store passwords in plaintext. They could have them encrypted and are decrypting them when they send them to you. Of course this is bad practice.
– Greg Schmit
6 hours ago
1
And they claim, at least, that they don't store passwords in plaintext: i.imgur.com/9qrVPrm.png (again, not disputing that this is bad practice).
– Greg Schmit
6 hours ago
@GregSchmit: Regardless of whether the password is stored plaintext in the auth database, it is stored plaintext in HostGator's e-mail server, potentially transmitted in plaintext across the Internet, and potentially stored plaintext at the recipient e-mail server. I say potentially because it largely depends on the domain where you receive your HostGator e-mail and how the server handling that domain is configured.
– Ben Voigt
3 hours ago
1
@BenVoigt We already know for a fact that the plaintext password was emailed, so that's irrelevant. The question is whether they are storing that in plaintext in their database. The OP wouldn't have asked "is this password stored in plaintext on an email server somewhere", because that would be a stupid question to ask given that the password was emailed.
– Greg Schmit
3 hours ago
@GregSchmit: Why can't OP ask a question he already knows the answer to? That's Socratic method. The goal is not to learn the answer, it's to make the other person aware of the problem.
– Ben Voigt
3 hours ago
|
show 1 more comment
1
I realize that this is a semantic point, but I don't see how this proves that they store passwords in plaintext. They could have them encrypted and are decrypting them when they send them to you. Of course this is bad practice.
– Greg Schmit
6 hours ago
1
And they claim, at least, that they don't store passwords in plaintext: i.imgur.com/9qrVPrm.png (again, not disputing that this is bad practice).
– Greg Schmit
6 hours ago
@GregSchmit: Regardless of whether the password is stored plaintext in the auth database, it is stored plaintext in HostGator's e-mail server, potentially transmitted in plaintext across the Internet, and potentially stored plaintext at the recipient e-mail server. I say potentially because it largely depends on the domain where you receive your HostGator e-mail and how the server handling that domain is configured.
– Ben Voigt
3 hours ago
1
@BenVoigt We already know for a fact that the plaintext password was emailed, so that's irrelevant. The question is whether they are storing that in plaintext in their database. The OP wouldn't have asked "is this password stored in plaintext on an email server somewhere", because that would be a stupid question to ask given that the password was emailed.
– Greg Schmit
3 hours ago
@GregSchmit: Why can't OP ask a question he already knows the answer to? That's Socratic method. The goal is not to learn the answer, it's to make the other person aware of the problem.
– Ben Voigt
3 hours ago
1
1
I realize that this is a semantic point, but I don't see how this proves that they store passwords in plaintext. They could have them encrypted and are decrypting them when they send them to you. Of course this is bad practice.
– Greg Schmit
6 hours ago
I realize that this is a semantic point, but I don't see how this proves that they store passwords in plaintext. They could have them encrypted and are decrypting them when they send them to you. Of course this is bad practice.
– Greg Schmit
6 hours ago
1
1
And they claim, at least, that they don't store passwords in plaintext: i.imgur.com/9qrVPrm.png (again, not disputing that this is bad practice).
– Greg Schmit
6 hours ago
And they claim, at least, that they don't store passwords in plaintext: i.imgur.com/9qrVPrm.png (again, not disputing that this is bad practice).
– Greg Schmit
6 hours ago
@GregSchmit: Regardless of whether the password is stored plaintext in the auth database, it is stored plaintext in HostGator's e-mail server, potentially transmitted in plaintext across the Internet, and potentially stored plaintext at the recipient e-mail server. I say potentially because it largely depends on the domain where you receive your HostGator e-mail and how the server handling that domain is configured.
– Ben Voigt
3 hours ago
@GregSchmit: Regardless of whether the password is stored plaintext in the auth database, it is stored plaintext in HostGator's e-mail server, potentially transmitted in plaintext across the Internet, and potentially stored plaintext at the recipient e-mail server. I say potentially because it largely depends on the domain where you receive your HostGator e-mail and how the server handling that domain is configured.
– Ben Voigt
3 hours ago
1
1
@BenVoigt We already know for a fact that the plaintext password was emailed, so that's irrelevant. The question is whether they are storing that in plaintext in their database. The OP wouldn't have asked "is this password stored in plaintext on an email server somewhere", because that would be a stupid question to ask given that the password was emailed.
– Greg Schmit
3 hours ago
@BenVoigt We already know for a fact that the plaintext password was emailed, so that's irrelevant. The question is whether they are storing that in plaintext in their database. The OP wouldn't have asked "is this password stored in plaintext on an email server somewhere", because that would be a stupid question to ask given that the password was emailed.
– Greg Schmit
3 hours ago
@GregSchmit: Why can't OP ask a question he already knows the answer to? That's Socratic method. The goal is not to learn the answer, it's to make the other person aware of the problem.
– Ben Voigt
3 hours ago
@GregSchmit: Why can't OP ask a question he already knows the answer to? That's Socratic method. The goal is not to learn the answer, it's to make the other person aware of the problem.
– Ben Voigt
3 hours ago
|
show 1 more comment
If the company rep's response is true, the Password is stored as an encrypted text. This makes the plain text password in unprompted email a bigger concern.
is it safe to assume that my password is stored in their database as plain text?
The company representative explicitly told that they are not storing the password in plain text. Assuming that he is telling the truth, my conclusion is that they are storing the password in encrypted text. They are better than plain text passwords but they are still insecure. Hashing and salting is the best way to store passwords.
If the stored password is encrypted, the biggest concern here is not the way it is stored but the way it is transmitted, in plain text on an email when the user did not request any.
do you have any suggestions on how to address this issue with the
provider?
You can ask the company to change the following (in the order of priority)
- Stop sending passwords over email.
- Provide Reset password option instead of recovering it.
- Replace encrypting passwords with Hashing and Salting.
In response to comments,
- Yes, there is high chance that the rep is lying or didn't know what he is talking about. But there is also a possibility that he was telling the truth. This answer deals with that scenario.
- I consider transmission of passwords as a bigger problem to storage because the OP was sent the password in an email when he did not ask for any.
- I have seen systems that store passwords in an encrypted text and send them to users upon request. They are not secure, but they do exist. Just because you received your info in plain text does not guarantee it is stored that way too.
40
"No, the company representative explicitly told that they are not storing the password in plain text" since when can you blindly trust what a low level rep says about a large company?
– MindSwipe
yesterday
36
@KolappanNathan Given that that same employee considers sending passwords via email to be a safe practice, there's very little reason to assume that rep is a trustworthy source of information.
– Beofett
yesterday
17
"Assuming he is telling the truth" implies he is either truthful and correct or lying. The reality is likely a third option: he doesn't actually know the answer and, like many reps, is simply trying to make the person on the other end happy. Never attribute to malice what can easily be explained by ignorance. The fact that the rep doesn't even know how to spell encryption (the way they spelled it clearly wasn't the result of a simply typo) is a strong indication that they are simply ignorant of this topic and don't know anything about it.
– Conor Mancone
yesterday
2
@ConorMancone That is possible and an answer already exists for such a possibility. My answer deals with an another possible scenario that the password is encrypted. It is a possible scenario. No one can tell for 100% percent that the password is in plain text. What is wrong about writing answers for an another possible scenario? The typo does not indicate anything. He misspelled a single letter!!!
– Kolappan Nathan
yesterday
2
@ConorMancone The OP said that he received the password in email when he did not ask for any. He could have abandoned his email. I consider transmission to be biggest issue. I agree with the fact that encrypting passwords is insecure too. No disagreements there.
– Kolappan Nathan
yesterday
|
show 7 more comments
If the company rep's response is true, the Password is stored as an encrypted text. This makes the plain text password in unprompted email a bigger concern.
is it safe to assume that my password is stored in their database as plain text?
The company representative explicitly told that they are not storing the password in plain text. Assuming that he is telling the truth, my conclusion is that they are storing the password in encrypted text. They are better than plain text passwords but they are still insecure. Hashing and salting is the best way to store passwords.
If the stored password is encrypted, the biggest concern here is not the way it is stored but the way it is transmitted, in plain text on an email when the user did not request any.
do you have any suggestions on how to address this issue with the
provider?
You can ask the company to change the following (in the order of priority)
- Stop sending passwords over email.
- Provide Reset password option instead of recovering it.
- Replace encrypting passwords with Hashing and Salting.
In response to comments,
- Yes, there is high chance that the rep is lying or didn't know what he is talking about. But there is also a possibility that he was telling the truth. This answer deals with that scenario.
- I consider transmission of passwords as a bigger problem to storage because the OP was sent the password in an email when he did not ask for any.
- I have seen systems that store passwords in an encrypted text and send them to users upon request. They are not secure, but they do exist. Just because you received your info in plain text does not guarantee it is stored that way too.
40
"No, the company representative explicitly told that they are not storing the password in plain text" since when can you blindly trust what a low level rep says about a large company?
– MindSwipe
yesterday
36
@KolappanNathan Given that that same employee considers sending passwords via email to be a safe practice, there's very little reason to assume that rep is a trustworthy source of information.
– Beofett
yesterday
17
"Assuming he is telling the truth" implies he is either truthful and correct or lying. The reality is likely a third option: he doesn't actually know the answer and, like many reps, is simply trying to make the person on the other end happy. Never attribute to malice what can easily be explained by ignorance. The fact that the rep doesn't even know how to spell encryption (the way they spelled it clearly wasn't the result of a simply typo) is a strong indication that they are simply ignorant of this topic and don't know anything about it.
– Conor Mancone
yesterday
2
@ConorMancone That is possible and an answer already exists for such a possibility. My answer deals with an another possible scenario that the password is encrypted. It is a possible scenario. No one can tell for 100% percent that the password is in plain text. What is wrong about writing answers for an another possible scenario? The typo does not indicate anything. He misspelled a single letter!!!
– Kolappan Nathan
yesterday
2
@ConorMancone The OP said that he received the password in email when he did not ask for any. He could have abandoned his email. I consider transmission to be biggest issue. I agree with the fact that encrypting passwords is insecure too. No disagreements there.
– Kolappan Nathan
yesterday
|
show 7 more comments
If the company rep's response is true, the Password is stored as an encrypted text. This makes the plain text password in unprompted email a bigger concern.
is it safe to assume that my password is stored in their database as plain text?
The company representative explicitly told that they are not storing the password in plain text. Assuming that he is telling the truth, my conclusion is that they are storing the password in encrypted text. They are better than plain text passwords but they are still insecure. Hashing and salting is the best way to store passwords.
If the stored password is encrypted, the biggest concern here is not the way it is stored but the way it is transmitted, in plain text on an email when the user did not request any.
do you have any suggestions on how to address this issue with the
provider?
You can ask the company to change the following (in the order of priority)
- Stop sending passwords over email.
- Provide Reset password option instead of recovering it.
- Replace encrypting passwords with Hashing and Salting.
In response to comments,
- Yes, there is high chance that the rep is lying or didn't know what he is talking about. But there is also a possibility that he was telling the truth. This answer deals with that scenario.
- I consider transmission of passwords as a bigger problem to storage because the OP was sent the password in an email when he did not ask for any.
- I have seen systems that store passwords in an encrypted text and send them to users upon request. They are not secure, but they do exist. Just because you received your info in plain text does not guarantee it is stored that way too.
If the company rep's response is true, the Password is stored as an encrypted text. This makes the plain text password in unprompted email a bigger concern.
is it safe to assume that my password is stored in their database as plain text?
The company representative explicitly told that they are not storing the password in plain text. Assuming that he is telling the truth, my conclusion is that they are storing the password in encrypted text. They are better than plain text passwords but they are still insecure. Hashing and salting is the best way to store passwords.
If the stored password is encrypted, the biggest concern here is not the way it is stored but the way it is transmitted, in plain text on an email when the user did not request any.
do you have any suggestions on how to address this issue with the
provider?
You can ask the company to change the following (in the order of priority)
- Stop sending passwords over email.
- Provide Reset password option instead of recovering it.
- Replace encrypting passwords with Hashing and Salting.
In response to comments,
- Yes, there is high chance that the rep is lying or didn't know what he is talking about. But there is also a possibility that he was telling the truth. This answer deals with that scenario.
- I consider transmission of passwords as a bigger problem to storage because the OP was sent the password in an email when he did not ask for any.
- I have seen systems that store passwords in an encrypted text and send them to users upon request. They are not secure, but they do exist. Just because you received your info in plain text does not guarantee it is stored that way too.
edited 15 hours ago
answered yesterday
Kolappan NathanKolappan Nathan
1,643618
1,643618
40
"No, the company representative explicitly told that they are not storing the password in plain text" since when can you blindly trust what a low level rep says about a large company?
– MindSwipe
yesterday
36
@KolappanNathan Given that that same employee considers sending passwords via email to be a safe practice, there's very little reason to assume that rep is a trustworthy source of information.
– Beofett
yesterday
17
"Assuming he is telling the truth" implies he is either truthful and correct or lying. The reality is likely a third option: he doesn't actually know the answer and, like many reps, is simply trying to make the person on the other end happy. Never attribute to malice what can easily be explained by ignorance. The fact that the rep doesn't even know how to spell encryption (the way they spelled it clearly wasn't the result of a simply typo) is a strong indication that they are simply ignorant of this topic and don't know anything about it.
– Conor Mancone
yesterday
2
@ConorMancone That is possible and an answer already exists for such a possibility. My answer deals with an another possible scenario that the password is encrypted. It is a possible scenario. No one can tell for 100% percent that the password is in plain text. What is wrong about writing answers for an another possible scenario? The typo does not indicate anything. He misspelled a single letter!!!
– Kolappan Nathan
yesterday
2
@ConorMancone The OP said that he received the password in email when he did not ask for any. He could have abandoned his email. I consider transmission to be biggest issue. I agree with the fact that encrypting passwords is insecure too. No disagreements there.
– Kolappan Nathan
yesterday
|
show 7 more comments
40
"No, the company representative explicitly told that they are not storing the password in plain text" since when can you blindly trust what a low level rep says about a large company?
– MindSwipe
yesterday
36
@KolappanNathan Given that that same employee considers sending passwords via email to be a safe practice, there's very little reason to assume that rep is a trustworthy source of information.
– Beofett
yesterday
17
"Assuming he is telling the truth" implies he is either truthful and correct or lying. The reality is likely a third option: he doesn't actually know the answer and, like many reps, is simply trying to make the person on the other end happy. Never attribute to malice what can easily be explained by ignorance. The fact that the rep doesn't even know how to spell encryption (the way they spelled it clearly wasn't the result of a simply typo) is a strong indication that they are simply ignorant of this topic and don't know anything about it.
– Conor Mancone
yesterday
2
@ConorMancone That is possible and an answer already exists for such a possibility. My answer deals with an another possible scenario that the password is encrypted. It is a possible scenario. No one can tell for 100% percent that the password is in plain text. What is wrong about writing answers for an another possible scenario? The typo does not indicate anything. He misspelled a single letter!!!
– Kolappan Nathan
yesterday
2
@ConorMancone The OP said that he received the password in email when he did not ask for any. He could have abandoned his email. I consider transmission to be biggest issue. I agree with the fact that encrypting passwords is insecure too. No disagreements there.
– Kolappan Nathan
yesterday
40
40
"No, the company representative explicitly told that they are not storing the password in plain text" since when can you blindly trust what a low level rep says about a large company?
– MindSwipe
yesterday
"No, the company representative explicitly told that they are not storing the password in plain text" since when can you blindly trust what a low level rep says about a large company?
– MindSwipe
yesterday
36
36
@KolappanNathan Given that that same employee considers sending passwords via email to be a safe practice, there's very little reason to assume that rep is a trustworthy source of information.
– Beofett
yesterday
@KolappanNathan Given that that same employee considers sending passwords via email to be a safe practice, there's very little reason to assume that rep is a trustworthy source of information.
– Beofett
yesterday
17
17
"Assuming he is telling the truth" implies he is either truthful and correct or lying. The reality is likely a third option: he doesn't actually know the answer and, like many reps, is simply trying to make the person on the other end happy. Never attribute to malice what can easily be explained by ignorance. The fact that the rep doesn't even know how to spell encryption (the way they spelled it clearly wasn't the result of a simply typo) is a strong indication that they are simply ignorant of this topic and don't know anything about it.
– Conor Mancone
yesterday
"Assuming he is telling the truth" implies he is either truthful and correct or lying. The reality is likely a third option: he doesn't actually know the answer and, like many reps, is simply trying to make the person on the other end happy. Never attribute to malice what can easily be explained by ignorance. The fact that the rep doesn't even know how to spell encryption (the way they spelled it clearly wasn't the result of a simply typo) is a strong indication that they are simply ignorant of this topic and don't know anything about it.
– Conor Mancone
yesterday
2
2
@ConorMancone That is possible and an answer already exists for such a possibility. My answer deals with an another possible scenario that the password is encrypted. It is a possible scenario. No one can tell for 100% percent that the password is in plain text. What is wrong about writing answers for an another possible scenario? The typo does not indicate anything. He misspelled a single letter!!!
– Kolappan Nathan
yesterday
@ConorMancone That is possible and an answer already exists for such a possibility. My answer deals with an another possible scenario that the password is encrypted. It is a possible scenario. No one can tell for 100% percent that the password is in plain text. What is wrong about writing answers for an another possible scenario? The typo does not indicate anything. He misspelled a single letter!!!
– Kolappan Nathan
yesterday
2
2
@ConorMancone The OP said that he received the password in email when he did not ask for any. He could have abandoned his email. I consider transmission to be biggest issue. I agree with the fact that encrypting passwords is insecure too. No disagreements there.
– Kolappan Nathan
yesterday
@ConorMancone The OP said that he received the password in email when he did not ask for any. He could have abandoned his email. I consider transmission to be biggest issue. I agree with the fact that encrypting passwords is insecure too. No disagreements there.
– Kolappan Nathan
yesterday
|
show 7 more comments
Marquizzo is a new contributor. Be nice, and check out our Code of Conduct.
Marquizzo is a new contributor. Be nice, and check out our Code of Conduct.
Marquizzo is a new contributor. Be nice, and check out our Code of Conduct.
Marquizzo is a new contributor. Be nice, and check out our Code of Conduct.
Thanks for contributing an answer to Information Security Stack Exchange!
- Please be sure to answer the question. Provide details and share your research!
But avoid …
- Asking for help, clarification, or responding to other answers.
- Making statements based on opinion; back them up with references or personal experience.
To learn more, see our tips on writing great answers.
Sign up or log in
StackExchange.ready(function ()
StackExchange.helpers.onClickDraftSave('#login-link');
);
Sign up using Google
Sign up using Facebook
Sign up using Email and Password
Post as a guest
Required, but never shown
StackExchange.ready(
function ()
StackExchange.openid.initPostLogin('.new-post-login', 'https%3a%2f%2fsecurity.stackexchange.com%2fquestions%2f206186%2fis-hostgator-storing-my-password-in-plaintext%23new-answer', 'question_page');
);
Post as a guest
Required, but never shown
Sign up or log in
StackExchange.ready(function ()
StackExchange.helpers.onClickDraftSave('#login-link');
);
Sign up using Google
Sign up using Facebook
Sign up using Email and Password
Post as a guest
Required, but never shown
Sign up or log in
StackExchange.ready(function ()
StackExchange.helpers.onClickDraftSave('#login-link');
);
Sign up using Google
Sign up using Facebook
Sign up using Email and Password
Post as a guest
Required, but never shown
Sign up or log in
StackExchange.ready(function ()
StackExchange.helpers.onClickDraftSave('#login-link');
);
Sign up using Google
Sign up using Facebook
Sign up using Email and Password
Sign up using Google
Sign up using Facebook
Sign up using Email and Password
Post as a guest
Required, but never shown
Required, but never shown
Required, but never shown
Required, but never shown
Required, but never shown
Required, but never shown
Required, but never shown
Required, but never shown
Required, but never shown
Comments are not for extended discussion; this conversation has been moved to chat.
– Rory Alsop♦
9 hours ago